Pacific World War II Timeline
Editor’s note: Contributed by the War in the Pacific National Historical Park. Photos from the Micronesian Area Research Center, National Archives, Naval History and Heritage Command, The Japan Times, War in the Pacific, and Wikimedia Commons collections. Download the timeline for more information on the images here.
Timeline
1940

Relations between Japan and the United States deteriorate as America initiates first trade embargo on war-related goods to the Asian nation. Image information: Hull, Nomura, and Kurusu.
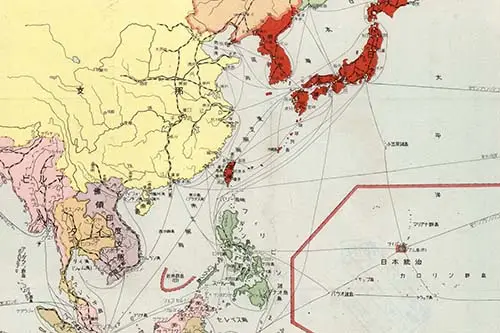
Japan declares the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere concept desiring to ensure its dominance in Asia and the Pacific and its ability to take raw materials from its neighbors. Japan’s determination to realize the concept through a policy of expansion through aggression would lead to direct conflict with numerous nations, particularly the United States and Britain. Image information: Map of Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere 1941.
1941

US Navy dependents and civilians are evacuated by US Navy Captain George Johnson McMillin. They boarded the USS Henderson for Hawai’i. Image information: USS Henderson.

Aircraft of the Japanese navy launch a surprise strike on US military facilities on Oahu, Hawai'i. The attack cripples the navy at Pearl Harbor as the US is thrust into World War II. Killed were more than 2,500 Americans, 21 warships were either destroyed or damaged, 169 aircraft demolished. The attack and others nearly simultaneous across the Pacific, including Guam, and Asia would eventually net Japan an empire of more than 20 million square miles. Image information: USS SHAW Exploding During the Japanese Raid on Pearl Harbor.
Across the dateline and shortly after the Pearl Harbor attack, Japanese dive-bombers from bases in Saipan, the Marshalls, and Formosa, strike Guam, Wake Island, and the Philippines. On this day in the US mainland, President Roosevelt, elected 5 November, describes the attack on Pearl Harbor as “a date which will live in infamy.” US formally declares war on Japan as do Canada and Great Britain. Image information: Japanese Offensive, December 1941.


In the darkness of early morning, troops of Japan’s South Seas Detachment invade Guam; one group of 400 soldiers lands at Dungca’s Beach in Tamuning, other units, totaling 5,500, come ashore south of Hågat village, at Togcha and at Tumon. After a brief but futile firefight at the Plaza de España between the Guam Insular Guard and the detachment, Capt. George McMillion, naval governor of Guam, surrenders the island to the Japanese about 7 am. Image information: Invasion of Guam courtesy of the Guam Public Library System.

Germany and Italy, partners with Japan since the signing of the Tripartite Pact in September 1940, declare war on the United States. The United States answers in kind. Image information: Signing Ceremony of the Tripartite Pact of the Axis Powers.

On 23 December, after repulsing an initial Japanese landing on 11 December, US sailors, Marines and others surrender Wake Island. Forty-Five CHamorus/Chamorros participate in the island’s defense; 10 of those die in the 12 day siege. Initial Japanese force receives support by some ships and aircraft involved in the 7 December attack on Pearl Harbor. On Christmas Day the Japanese capture Hong Kong. Image information: Wake Island Attack.
1942

American military and civilian personnel, Navy nurses, as well as American and Spanish priests on Guam are forced to march to Piti and board the ship Argentina Maru. Their destination: Prisoner of war camps in Japan. Image information: Argentina Maru Brazil Maru.

General Douglas MacArthur, ordered by President Roosevelt to leave the Philippines 11 March evades capture by Japanese forces and arrives in Australia. There, he makes a vow and one of the war’s most famous declarations: "I came through and I shall return." Image information: General Douglas MacArthur and His Chief of Staff Major General Sutherland.

President Roosevelt appoints MacArthur as Supreme Commander Southwest Pacific Area and Admiral Chester W. Nimitz as Commander-in-Chief, Pacific Ocean Area. Image information: MacArthur and Nimitz.

American and Filipino forces on Battan surrender to the Japanese army under General Homma Masaharu. The “Bataan Death March” begins. About 76,000 American and Filipino survivors are forced to march 60 miles to POW camps. As so many are in a weakened and starved state, 5,000 perish; still more die in the camps. Image information: March of Death from WAPA.

Launched from the carrier Hornet, 16 B-25 Mitchell bombers, commanded by Lt. Col Jimmy Doolittle, attack military facilities in several Japanese cities. The air strike uplifts America from coast to coast, as the nation is still in shock from Pearl Harbor and the reality of war. Image information: Doolittle Raid on Japan, 18 April 1942.

With the island fortress of Corregidor succumbing to the siege by the Japanese Imperial army, General Jonathan Wainwright, commander of US and Filipino soldiers in the place of MacArthur, surrenders. The Philippines falls. Image information: Philippine Invasion, 1941-1942.

US Navy carriers under Admiral Nimitz confront carriers of a fleet commanded by Japan’s Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto in the Battle of Midway. After an initial Japanese air strike on Midday Island, US Navy pilots seize the advantage when they catch Japanese aircraft on carrier decks fueling and rearming. At battle’s end, sunk are the Japanese carriers Kaga, Soryu, Hiryu, and the Akagi. Although the Yorktown sinks following the battle, the US victory would prove to be a critical turning point of the war in the Pacific. Image information: Battle of Midway, June 1942.


In first US amphibious operation of war, the 1st Marine Division lands at Guadalcanal, the largest island of the Solomons. Unveiled is the tactical blueprint for taking the war through the Pacific to Japan; a landing force attacks as aircraft and naval gunfire, in close support, strike at enemy ground forces. The Japanese, after months of bitter fighting, withdraw from Guadalcanal in February 1943. Image information: Guadalcanal-Tulagi Operation, August 1942.

Naval forces collide in the sea battle of Guadalcanal. The Japanese battleships Hiei and Kirishima are sunk. The sinking follow those of the Japanese carrier Ryujo on 24 August, and the American carriers Wasp, on 15 September and the Hornet on 27 October. Though losing ships, the US accomplishes a strategic victory as the battle demonstrates the Japanese inability to resupply or reinforce troops at Guadalcanal. Image information: Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, 12-15 November 1942.
1943

At Buna and Gona in New Guinea, US and Australian troops catch Japanese forces in retreat from a failed campaign to take Port Moresby. The Allied counter attack ends the Japanese threat to Australia; the victory is the first decisive triumph on land for the Allies in the Pacific. Image information: Porters on Muddy Track, Buna.

US forces land and retake Attu, in the far western Aleutian islands, from the Japanese, who occupied the island and nearby Kiska since 7 June 1942. (Kiska was taken 15 August 1943 without a battle because Japanese had evacuated secretly under the cover of fog more than two weeks earlier.) Image information: Attu Invasion, May 1943.

With the Navy securing control of the Bismarck Sea in March, MacArthur, landing in New Guinea, and Admiral William “Bull” Halsey, his forces coming ashore in the eastern Solomons, put into motion Operation Cartwheel. The operation, which establishes airfields from which to bomb the major Japanese base of Rabaul, takes months to accomplish but dooms the base. Image information: New Guinea.

Still trying to isolate Rabaul, US forces under Halsey invade Bougainville; among the units involved is the 3rd Marine Division, destined to invade Guam. Securing Bougainville takes until April 1944 but the operation sustains US superiority in the region. Image information: South Pacific Force.

Nimitiz begins “island-hopping” in the central Pacific through Micronesia. The 2nd Marine Division invades heavily fortified Tarawa, and the Army’s 27th Infantry Division lands on Main (both part of Kiribati, formerly the Gilbert Islands). The battles in this eastern-most part of the Micronesian Region are costly; while only 60 men were killed at tiny Makin, 1,056 die in 76 hours of fierce fighting at Tarawa. Future invasions, in the Marshalls and Marianas, feature better intelligence, better ship-to-shore transfer of troops, equipment and supplies. Image information: Adm. Nimitz and Men Inspect Betio Island, 17 November 1943.

Forces under MacArthur achieve landings at New Britain in the Bismarck archipelago. From there, MacArthur begins to secure the western Solomons, New Guinea, and eventually the Philippines. With the operations of MacArthur and Halsey complementing each other in the southwest Pacific, the Allies mount another offensive to nearly parallel Nimitz’s path through the central Pacific toward Japan. Image information: Cape Gloucester Invasion, December 1943.
1944

The drive by US forces through Micronesia and the central Pacific continues. In the Marshall Islands, the 4th Marine Division and the Army’s 7th Infantry Division attack Japanese forces on Kwajalein and on Roi Namur. Also invaded and captured is Majuro, the atoll which is the present day capital of the Republic of the Marshall Islands. The costly lessons of Tarawa pay off; only 334 men are killed in the landings. Image information: Marshall Islands Campaign, January-February 1944.

US campaign seizes the Admiralty islands north of Papua New Guinea. US forces now greatly hinder Japanese supply lines from Rabaul in the south Pacific to Truk (now Chuuk, Federated States of Micronesia), Japan’s major naval base in the central Pacific. The path is clear for the capture of the Marianas. Image information: Admiralties Invasion, 1944.

Borne by carriers of the fleet of Admiral Marc Mitscher, Navy aircraft conduct a series of raids on Chuuk, a major Japanese naval installation in the western Pacific. One raid was the first nighttime bombing mission by the Navy. Japanese losses from the raids are heavy; 275 aircraft, 10 ships and 31 merchant ships. Ship tonnage lost - 200,000 tons - was the highest in the war for a single action. Image information: Truk Raid.

US forces under Nimitz continue westward through Micronesia toward Japan. Another atoll is taken when Eniwetok is invaded and taken by the 2nd Marine Division. More than 250 men are killed, light when compared to Tarawa. Image information: Eniwetok Operation, February 1944.

US carriers carry on their program of destruction, this time their pilots unleashing their firepower in raids on the Marianas. US Navy pilots down 168 aircraft and sink two freighters while losing only six aircraft. Image information: Marianas Operation, June 1944.

The 2nd and 4th Marine Divisions land on Saipan in the Marianas, beginning the first battle fought in Japan’s inner defense line. US forces find fighting extremely difficult against a Japanese enemy growing desperate. Americans complete capture of Saipan on 9 July. Image information: Wreckage in Garapan, Saipan, courtesy of WAPA.

West of the Mariana islands, the naval Battle of the Philippine Sea is joined when the US fleet of Admiral Mitscher intercepts the Japanese fleet of Vice Admiral Jisaburo Ozawa. Ozawa’s force is rushing to catch the American invasion force on the beaches of Saipan. In what would be called “The Great Marianas Turkey Shoot”, US carrier pilots destroy more than 400 enemy plans, sink a carrier and other vessels. Mitscher’s two subs join in the devastating defeat of the Japanese force by sinking two carriers. American losses were more than 100 aircraft and slight damage to the battleship South Dakota. Image information: Battle of the Philippine Sea, June 1944.

More than two and half years after Pearl Harbor, the US returns to Guam to liberate the island from Japan. Confronted by intense fire from Japanese defenders, the 3rd Marine Division lands at Asan, and to the south, the 1st Provisional Marine Brigade, followed by the Army’s 77th Infantry Division, goes ashore on the beaches in Hågat. Image information: Marines Pinned Down (USMC #87283).

Three days after US forces land on Guam, and using Saipan as a staging area, the 4th Marine Division invades Tinian. Feigning a landing on the beaches near the island’s town, the Marines instead establish a beachhead at an undefended spot in the island’s northwest, a spot thought to be too small by the Japanese defenders for an invasion force. The landing’s success led to the island being declared secure eight days later. Image information: Saipan Invasion, June 1944.


In Guam, two American invasion forces link up at Mount Tenjo. With the final beach line secured, US troops advance to the north, chasing retreating enemy soldiers. Image information: March North from the Micronesian Area Research Center (MARC).

The Battle of Aitape in Papua New Guinea ends after a month of fighting. Unable to capitalize on a breakthrough of Allied lines, Japanese troops under General Adachi Hatazo falter, then are fatally enveloped in a counterattack. More than 10,000 Japanese soldiers perish in the last battle of Papua New Guinea. Image information: Hollandia, New Guinea, Operation, April 1944.

General Roy Geiger declares Guam secure by American forces. Military officials are now tasked with two duties: providing car to war-ravaged island residents and molding Guam as a staging area for naval and air operations against Japan. Image information: US Marine Barracks, Orote, July 1944.

US forces hit another Japanese stronghold, this time Palau. There the 1st Marine Division invades Peleliu and the 81st Infantry Division strikes at Angaur. But the battle of Peleliu continues for weeks and is reminiscent of Tarawa’s heavy fortifications but with a twist - Peleliu possesses caves. At battle’s end, the dead: nearly 1,300 Marines and almost 300 soldiers from units called in to relieve the worn and ragged men of the Corps. Image information: Angaur Operation, September 1944.

MacArthur makes good on his vow to return to the Philippines as four US Army division land at Leyte. By February US forces have landed in Luzon and go on to occupy Manila. Image information: Invasion of Leyte, October 1944.

The Battle of Leyte Gulf, comprised of four separate engagements and the largest of the war, results in devastating defeat of the Japanese navy. Four Japanese carriers are sunk as the US solidifies its ability to retake the Philippines. For the first time “kamikazes” - pilots on suicide missions - are send into battle in a desperate attempt to halt the US advance toward Japan. Image information: Battle of Leyte Gulf, October 1944.

The siege of Iwo Jima nearly takes a month to complete. The volcanic isle leaves behind a legacy written in blood by the 3rd, 4th, and 5th Marine Divisions; US casualties are 6,800 dead, 20,000 wounded. There are practically no survivors of the 21,000 Japanese defenders. Image information: Photo Montage of Fifth Marine Division Cemetery on Iwo Jima.

With American forces nearing the Japanese home islands, the Japanese up the ante at Okinawa. Kamikazes spearhead the defense of the homeland, and nearly 2,000 soar to attack the US fleet supporting the invasion force. It is bloody at battle’s end; 12,500 American troops and 110,000 Japanese dead. Image information: Okinawa Campaign, March-June 1945.
1945

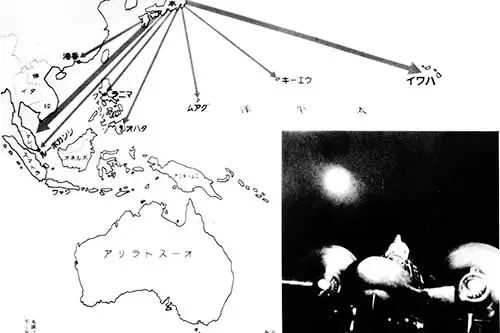
Three months after Germany has capitulated to the Allies, US officials desire to end the war quickly and without a bloody invasion of the Japanese homeland. It is decided to utilize a secret and terrible weapon. The “Enola Gay”, a B-29 bomber of the 509th Composite Group based in Tinian, drops the first atomic bomb in history on Hiroshima. Image information: Hiroshima, Japan.

The decision is made to unleash another atomic bomb, this time on Nagasaki. Bock’s car, another B-29 bomber of the 509th Composite Group on Tinian, drops the weapon. In the two atomic bomb detonations, more than 100,000 people perish; still more will die from injuries and radiation. Image information: A-Bomb Damage in Nagasaki, Japan.

In a radio broadcast which was the first public speech by a Japanese emperor, Emperor Hirohito announces the surrender of Japan. Image information: Emperor Hirohito's Broadcast, The Japan Times.

The Japanese formally surrender to the Allied powers in a ceremony aboard the US battleship Missouri in Tokyo Bay. Image information: Surrender of Japan, Tokyo Bay.
